Posted on November 04 2023
Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates in the World
By , Editor
Updated May 01 2024
Introduction: Taxation is a fundamental aspect of any country's economic system, shaping its fiscal policies, wealth distribution, and overall economic prosperity. Some nations opt for a minimalistic approach to taxation, offering residents and businesses low tax rates to attract investment, stimulate economic growth, and encourage financial well-being. In this extensive article, we will delve into two categories: countries with the lowest tax rates in the world and developed countries with the lowest tax rates. By exploring these categories, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the various tax systems and their implications for both citizens and businesses.
Section 1: Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates in the World
1.1 United Arab Emirates
Overview: The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a prominent example of a nation with one of the lowest tax rates in the world. It boasts neither a personal income tax nor a corporate income tax.
Rationale: The UAE's minimal tax regime is designed to attract foreign investments, businesses, and skilled professionals. It has become a hub for expatriates seeking a tax-efficient environment.
1.2 Bermuda
Overview: Bermuda is another country known for its low tax rates. It does not impose a personal income tax and generates revenue through customs duties, payroll taxes, and license fees.
Rationale: Bermuda's tax system aligns with its status as a global financial center. The absence of personal income tax is appealing to international businesses and professionals.
1.3 Monaco
Overview: Monaco is a renowned destination for the wealthy, offering a luxurious lifestyle and beautiful landscapes. It does not impose personal income tax.
Rationale: Monaco's tax policies aim to attract high-net-worth individuals and businesses to its shores. The absence of personal income tax complements its reputation as a tax haven.
1.4 Bahamas
Overview: The Bahamas, a popular tourist destination, does not levy personal income tax. The country relies on revenue generated primarily from its thriving tourism sector.
Rationale: The Bahamas' tax policies encourage tourism and foreign investment. Its pristine beaches and tax advantages make it an attractive destination for both tourists and investors.
1.5 Cayman Islands
Overview: The Cayman Islands are famous for their natural beauty and vibrant marine life. They do not impose personal income tax.
Rationale: The absence of personal income tax makes the Cayman Islands an appealing location for financial institutions and offshore businesses.
Section 2: Developed Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates in the World
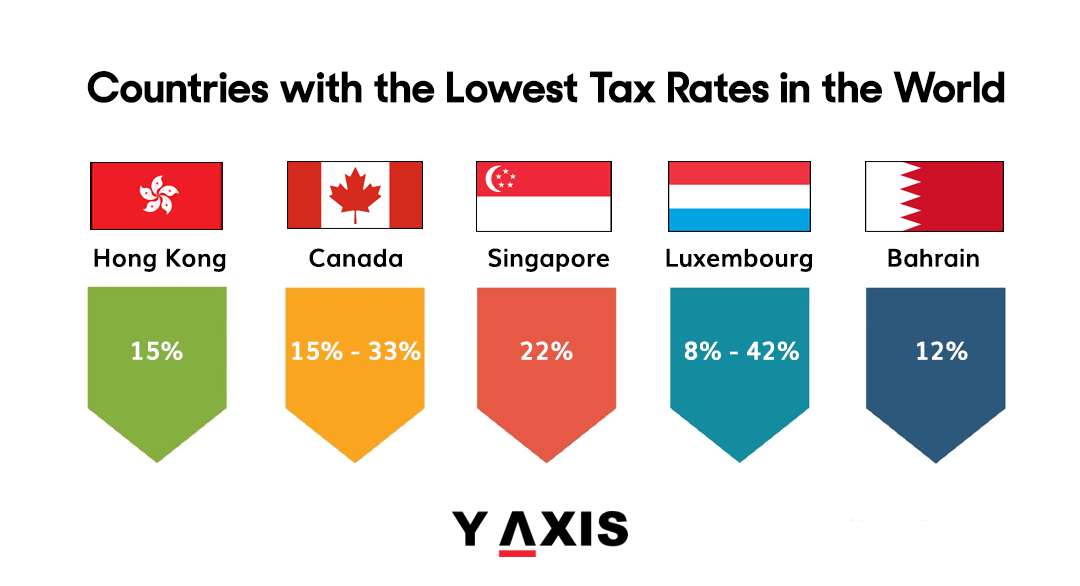
2.1 Hong Kong
Overview: Hong Kong is a developed city-state with a simple and low-tax system. The standard tax rate for individuals is 15%, with progressive rates for higher incomes.
Rationale: Hong Kong's low tax rates have contributed to its reputation as a global financial center and a hub for international business activities.
2.2 Canada
Overview: Canada, a developed nation, offers a variety of tax rates depending on income levels. Federal tax rates range from 15% to 33% for different income brackets.
Rationale: Canada's progressive tax system aims to provide essential services and support to its citizens while ensuring a competitive environment for businesses.
2.3 Singapore
Overview: Singapore's personal income tax rates start at 0% and progressively increase to a maximum of 22% for incomes above a specific threshold.
Rationale: Singapore's low tax rates have made it an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and multinational corporations, fostering economic growth and investment.
2.4 Luxembourg
Overview: Luxembourg has a progressive tax system with rates ranging from 8% to 42% on different income levels. A solidarity tax is also applied to higher earners.
Rationale: Luxembourg's tax system balances the need for public services with a competitive environment for the financial sector.
2.5 Bahrain
Overview: Bahrain has no personal income tax, but individuals employed in the country are subject to contributions to the Social Insurance Organization (SIO).
Rationale: Bahrain's tax policies aim to attract foreign workers while funding social services through contributions to the SIO.
Section 3: Implications and Considerations
3.1 Economic Prosperity
Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: The absence or minimal tax burden can attract foreign investment, stimulate economic growth, and lead to financial well-being for residents.
Developed Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: Balanced tax systems in developed countries aim to provide essential services while fostering economic growth, innovation, and competitiveness.
3.2 Attractiveness for Businesses
Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: These countries often serve as tax havens, drawing multinational corporations and financial institutions seeking favorable tax environments.
Developed Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: Developed nations with low tax rates can still attract businesses, especially those looking for stable and well-regulated markets.
3.3 Quality of Life
Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: The absence of personal income tax may contribute to a lower cost of living and higher disposable income for residents.
Developed Countries with the Lowest Tax Rates: Developed nations typically offer robust public services and a high quality of life for residents, which may offset higher tax rates.
Section 4: Conclusion
In the global landscape of taxation, the existence of countries with the lowest tax rates alongside developed countries with low tax rates showcases the diverse approaches nations take to manage their fiscal policies. Each system has its rationale and implications, affecting economic prosperity, business attractiveness, and the quality of life for residents. While countries with the lowest tax rates often serve as tax havens, developed nations with low tax rates seek to balance essential services and economic growth.
Ultimately, the choice between these tax systems depends on individual preferences, financial goals, and the specific circumstances of residents and businesses. It's crucial to conduct thorough research, consider the broader context of a country's economic policies, and possibly seek advice from financial experts before making decisions related to taxation and residency. Both low-tax jurisdictions and developed nations offer unique opportunities for financial success and a high quality of life, depending on your priorities and objectives.
Tags:
Lowest tax rates
countries
Tax-friendly nations
low-tax jurisdictions
Share
Options for you by Y-Axis
Get it on your mobile
Get News alerts
Contact Y-Axis