Posted on October 10 2025
New update on Germany Citizenship, check how you can apply.
By , Editor
Updated October 10 2025
Highlights: Germany Revises Citizenship Policy, Learn How You Can Apply
- Germany has repealed the fast-track citizenship rule that allowed well-integrated migrants to apply for citizenship in three years.
- The decision was backed by 450 lawmakers, with 134 opposing the repeal.
- The centre-right government under Chancellor Friedrich Merz led the move to reinforce national integration standards.
- The SPD, which introduced the earlier law, supported the repeal, noting the provision was rarely used.
- Germany will continue to allow dual citizenship and maintain a five-year residency requirement for naturalisation.
*Want to apply for German Citizenship? Talk to Y-Axis for complete immigration assistance.
Germany Revises Citizenship Policy to Strengthen Skilled Migration Framework
Germany’s latest citizenship reform represents a course correction rather than a restriction. While the fast-track route is no longer available, the country remains committed to attracting global talent through structured migration programs.
The Bundestag (German Parliament) recently voted to repeal the fast-track citizenship provision that was introduced by the previous SPD-led government. The now-repealed law allowed migrants who demonstrated strong integration, through employment, language proficiency, and civic participation, to apply for citizenship after three years, instead of the standard five.
This provision was designed to make Germany a top destination for global talent and to help fill the country’s chronic labour shortages. Germany, the largest economy in Europe, continues to face a shortfall of around 400,000 skilled workers annually, particularly in engineering, healthcare, and IT sectors.
*Want to settle in Germany? Sign up with Y-Axis to guide you with the process.
Eligibility Criteria to Apply for German Citizenship under the New Rules
Following the repeal of the fast-track route, applicants must now meet specific eligibility conditions to qualify for German citizenship under the five-year standard residency rule. These criteria ensure that individuals seeking naturalisation are well-integrated, financially independent, and legally compliant.
Here’s who is eligible to apply under the updated rules:
- Minimum Residency Requirement
Applicants must have legally lived in Germany for at least five consecutive years on a valid residence permit. In some cases, this period may be reduced to three years for spouses of German citizens or individuals with exceptional integration achievements.
- Valid Residence Status
You must hold a valid residence permit or EU Blue Card at the time of application. Students, employees, entrepreneurs, and family members of residents are all eligible, provided they meet other criteria.
- Language Proficiency
Applicants must demonstrate at least B1-level proficiency in the German language, as defined by the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). This shows your ability to communicate effectively and participate in everyday life in Germany.
- Financial Independence
You must be able to support yourself and your dependents without relying on state welfare benefits. Proof of steady employment, self-employment, or financial resources is required.
- Clean Legal Record
A clear criminal record is mandatory. Even minor offences can affect eligibility, so applicants must submit a police clearance certificate as part of the process.
- Knowledge of German Society and Law
Applicants must pass the German Citizenship Test, which evaluates understanding of the country’s laws, democratic values, and social systems. The test includes 33 questions, and a minimum of 17 correct answers are needed to pass.
- Integration and Commitment to German Values
Applicants must show that they have integrated into German life, respect democratic principles, and are willing to uphold the German constitution.
- Dual Citizenship Provision
Germany continues to allow dual citizenship under the new rules. This means that Indian nationals who meet the requirements can hold German citizenship while retaining their Indian nationality once reciprocal arrangements are formalized.
Also, read…
Live & Work in Germany – Freelance Visa for Just ₹7,500
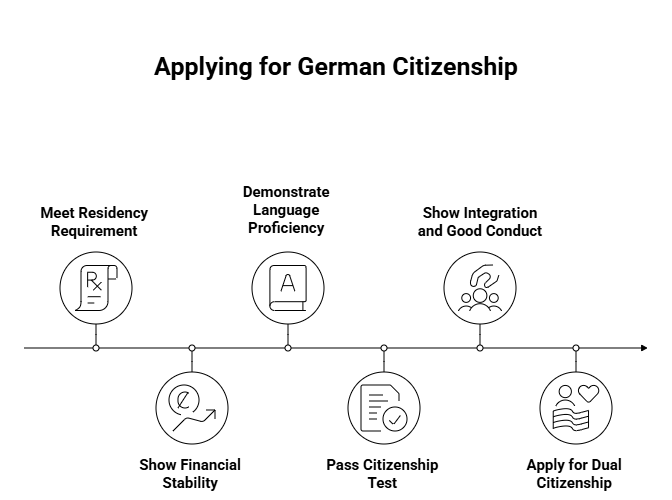
How to Apply for German Citizenship under the New Rules?
The latest update does not affect existing PR holders or long-term residents but restores the five-year route to citizenship for qualified applicants. Here’s how the process now works:
Step 1: Meet the Residency Requirement
You must have legally lived in Germany for at least five years on a valid residence permit.
Step 2: Show Financial Stability
Applicants must prove that they can support themselves financially without depending on state benefits.
Step 3: Demonstrate Language Proficiency
A minimum B1 level in the German language (as per the CEFR scale) is required to ensure you can integrate socially and professionally.
Step 4: Pass the Citizenship Test
Applicants must clear a test covering topics like German history, laws, and democratic values.
Step 5: Show Integration and Good Conduct
You must maintain a clean criminal record and demonstrate community involvement or cultural adaptation.
Step 6: Apply for Dual Citizenship (if eligible)
The new law continues to allow dual nationality, making it easier for non-EU nationals — including Indians — to retain ties to their home country while enjoying German citizenship rights.
Note: Processing times may vary, but most citizenship applications are reviewed within 6 to 12 months, depending on regional authorities and the completeness of documentation.
Why Germany Still Remains a Top Choice for Indians
Germany’s latest update to its citizenship law has sparked global attention, but for Indian migrants, the outlook remains highly positive. The country continues to encourage skilled migration, attract foreign students, and offer clear, long-term settlement pathways.
Here’s why Germany continues to stand out as a top destination for Indians:
- Strong demand for skilled workers: Germany faces an estimated 400,000 skilled worker shortage annually (Federal Employment Agency, 2024), creating vast opportunities for Indian professionals in IT, engineering, and healthcare.
- Stable and inclusive immigration system: Despite the repeal of the fast-track law, the five-year citizenship route and dual nationality provision make long-term settlement realistic for skilled migrants.
- Rising Indian presence: Over 200,000 Indians currently live and work in Germany, and more than 43,000 Indian students are enrolled in German universities — the highest number from any non-EU country (DAAD 2024).
- Favourable work and study pathways: Germany’s Blue Card program, Skilled Immigration Act, and post-study work options allow foreign talent to transition smoothly from education to employment and eventually citizenship.
- World-class living standards: With an employment rate above 77%, affordable education, and a strong economy, Germany offers an excellent quality of life for migrants and their families.

The repeal of the fast-track provision simply aligns Germany’s citizenship policy with its broader focus on integration, economic contribution, and community inclusion. For Indian migrants who aim to study, work, or build a long-term career in Europe, Germany remains one of the most secure and opportunity-driven destinations.
*Are you looking for step-by-step assistance for German immigration? Contact Y-Axis, the world’s No. 1 overseas immigration consultancy, for end-to-end support!
For recent Schengen updates, check out Y-Axis Schengen news page!
FAQs
1. What is the latest update on Germany’s citizenship law?
Germany’s parliament has repealed the fast-track citizenship route that allowed well-integrated migrants to apply for citizenship after just three years of residence. Under the new rule, the minimum residency requirement for naturalisation is now five years. The decision reflects the government’s focus on stronger integration standards and structured migration. Despite the repeal, Germany continues to allow dual citizenship and remains open to skilled professionals through its five-year pathway, work visa programs, and the Skilled Immigration Act, which simplifies migration for qualified non-EU workers.
2. Why did Germany end the fast-track citizenship route?
The fast-track citizenship route was repealed by the new centre-right government under Chancellor Friedrich Merz, which argued that the policy weakened immigration and integration standards. The previous SPD-led government had introduced the law to attract foreign professionals, but it was rarely used in practice. Interior Minister Alexander Dobrindt explained that the German passport should remain a reward for successful integration, not an incentive for irregular migration. The repeal aligns with the government’s goal to maintain stricter citizenship criteria while continuing to welcome skilled migrants to support the labour market.
3. What is the new residency requirement for German citizenship?
Under the updated citizenship rules, applicants must reside in Germany for at least five consecutive years before becoming eligible to apply for naturalisation. The previous fast-track option of three years for highly integrated migrants has been repealed. However, exceptions may apply for spouses of German citizens or individuals who demonstrate exceptional integration, where the period can still be reduced. This five-year rule aims to ensure that applicants have strong social, economic, and linguistic ties to Germany before being granted citizenship, maintaining a balance between openness and integration.
4. Does Germany still allow dual citizenship?
Yes. Despite the repeal of the fast-track citizenship route, Germany continues to allow dual citizenship for most applicants. This change, introduced under the 2024 Citizenship Law Reform, makes it easier for non-EU nationals, including Indians, to retain their original nationality while becoming German citizens. The policy reflects Germany’s effort to remain competitive in attracting global talent while acknowledging the growing international mobility of skilled professionals. Applicants who meet all residency, language, and integration requirements can apply for dual nationality without having to renounce their previous citizenship.
5. How can Indian professionals and students apply for German citizenship?
Indian nationals can apply for German citizenship after residing in Germany legally for at least five years with a valid residence permit. They must demonstrate B1-level proficiency in the German language, prove financial independence, and pass the German citizenship test. Additionally, applicants must have no criminal record and show integration into German society. Many Indians begin through work visas, student visas, or EU Blue Card programs, which can later lead to permanent residency and citizenship. Dual nationality is permitted, allowing Indian professionals to maintain strong ties to both countries.
6. Will the repeal affect current residents or PR holders in Germany?
No, the repeal does not negatively affect current residents, PR holders, or long-term visa holders in Germany. Those already living and working in Germany can continue on the five-year pathway to citizenship under the new rules. The change only removes the three-year fast-track option, which was previously available for highly integrated migrants. Existing visa categories such as the Blue Card, Skilled Immigration Act, and post-study work routes remain unchanged, ensuring that skilled professionals and students still have stable pathways to permanent residency and naturalisation.
7. What are the eligibility criteria for German citizenship under the new rules?
Applicants must have lived legally in Germany for at least five years, hold a valid residence permit, and prove B1-level proficiency in the German language. They must pass the citizenship test, which assesses knowledge of German history, law, and democratic principles. Additionally, applicants must show financial stability, have a clean criminal record, and demonstrate integration into German society. The new rules continue to allow dual citizenship, making it easier for skilled migrants — including Indians — to settle long-term and contribute to Germany’s growing economy.
8. What is the German citizenship test, and what does it include?
The German citizenship test is a mandatory part of the naturalisation process. It includes 33 multiple-choice questions covering German history, constitutional values, laws, and social systems. Applicants must correctly answer at least 17 questions to pass. The test ensures that new citizens understand the country’s democratic principles and civic responsibilities. Exemptions may apply for minors, elderly applicants, or individuals with disabilities. The test is available through the Federal Office for Migration and Refugees (BAMF) and must be completed before submitting the citizenship application.
9. How long does it take to process a German citizenship application?
The processing time for German citizenship applications typically ranges from six to twelve months, depending on the applicant’s location, the completeness of documentation, and local immigration office workload. Some regions may process applications faster if all required documents — including proof of residence, language certificates, and police clearance — are provided promptly. Applicants are advised to maintain continuous legal residence throughout the process. While the fast-track route has ended, the five-year citizenship pathway remains efficient and transparent under Germany’s reformed immigration system.
10. Why does Germany continue to attract Indian migrants despite policy changes?
Germany remains a top European destination for Indians due to its strong economy, world-class universities, and progressive migration policies. With over 200,000 Indian residents and 43,000 students in Germany, the country continues to welcome skilled professionals through programs like the EU Blue Card, Skilled Immigration Act, and post-study work options. The repeal of the fast-track law does not reduce opportunities; it instead emphasizes structured, long-term integration. For Indian workers and graduates seeking career growth, Germany offers stability, professional advancement, and a clear path to citizenship.
Tags:
Germany Citizenship
German immigration news
Migrate to Germany
German immigration
German citizenship law
German citizenship
German visas
fast-track citizenship law
Fast-track German citizenship law
Share
Options for you by Y-Axis
Get it on your mobile
Get News alerts
Contact Y-Axis

